Triage
Principles should be used whenever the number of casualties exceeds the capacity of skilled rescuers.
Triage is:
- A method of sorting casulaties into treatment priorities
- A dynamic process
- Reassessment is required to detect:
- Deteroriation
- Improvement
- Reassessed:
- At scene
- At CCS
- On arrival to hospital
- Etc
- Reassessment is required to detect:
Methods
Many triage tools exist. MIMMS describes the:
- Triage sieve
Rapidly sorts casualties into priorities based on physiological variables. Quick but crude. - Triage sort
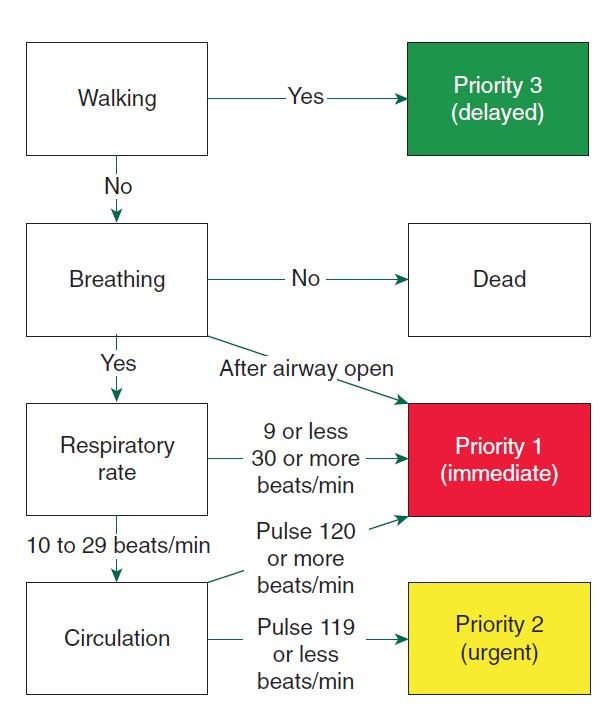
Triage Sieve
Straightforward protocol that is:
- Performed by anyone with limited training
- Reproducible
- Based on physiological assessments
Less prone to bias then anatomical systems. - Based on assessment of:
- Mobility
- Airway assessment
- Respiratory rate
- Circulation assessment
Capillary refil time ⩽2 seconds can also be used as an alternative to HR, though HR takes precedence.
Application to paediatrics:
- ↑ normal RR and HR in children will lead to relative over-triage of children
- Some feel this is beneficial to speed up evacuation of children
- Specific protocols for triaging of children exist
Paediatric Broselow tapes exist for triage protocols.
Classifications
- Tier 1
Immediate priority. Require immediate life-saving procedures. - Tier 2
Urgent priority. Require intervention within 2-4 hours. - Tier 3
Delayed priority. Intervention can be delayed ⩾4 hours.- Should be directed to a survivor reception centre
- Should continue to be monitored to ensure they do not deteriorate
- Tier 4
Expectant.- Casualty cannot survive despite best available care
- Treatment of casualty would divert medical resources from salvageable patients
- Only rarely activated
- Usually requires the incident to be uncompensated
- Decision to activate rests jointly with health service commanders at scene
Decision should be escalated to the highest level provided communication is intact, and in many instances will occur at Gold Command. - Avoiding the use of this category may cost additional lives
- May be revoked if resources become available
All T4 casualties then become T1.
Triage Sort
Controlled method triage based upon the Triage Revised Trauma Score, which uses the sum of scores from:
- Respiratory rate
- SBP
- GCS
| Score | Respiratory Rate |
|---|---|
| 10-29 | ⩾90 |
| ⩾30 | 76-89 |
| 6-9 | 50-75 |
| 1-5 | 1-49 |
| 0 | 0 |
Priority is then determined from the sum of scores in each category:
| Priority | TRTS Score |
|---|---|
| T1 | 1-10 |
| T2 | 11 |
| T3 | 12 |
| T4* | (1-3) |
| Dead | 0 |
^^If in use.*
Note that a live patient with a score of ⩽2 in any category will be T1.
Equipment
Triage categories can be identified with:
- Folding triage cards
- Coloured pegs
- Wristbands
References
- Advanced Life Support Group (Manchester, Kevin Mackway-Jones, and ProQuest (Firm). Major Incident Medical Management and Support the Practical Approach to Pre-Hospital Incident Command. Chichester, West Sussex, U.K.: Wiley-Blackwell, 2012.