G6PD Deficiency
G6PD is an X-linked enzyme deficiency that causes extravascular haemolysis under conditions of oxidative stress, notably:
- Physiological stress
- Surgery
- Sepsis
- DKA
- Foods
- Fava beans
Known as Favism. - Blueberries
- Fava beans
- Drugs
- Methylene blue
- Antibiotics
- Cotrimoxazole
- Sulfamethoxazole
- Nitrofurantoin
- Fluoroquinolones
- Primaquine
- Rasburicase
Epidemiology and Risk Factors
Pathophysiology
- G6PD is an enzyme that reduces NADP+ to NADPH by oxidising glucose-6-phosphate
- NADPH is used to regenerate glutathione, which is used by erythrocytes to repair oxidative damage
- Inadequate NADPH production results in:
- Glutathione depletion
- Unrepaired oxidative stress
Evident as inclusions, such as Heinz and Howel-Jolly bodies. - Extravascular haemolysis by the reticuloendothelial system
- Anaemia
- Jaundice
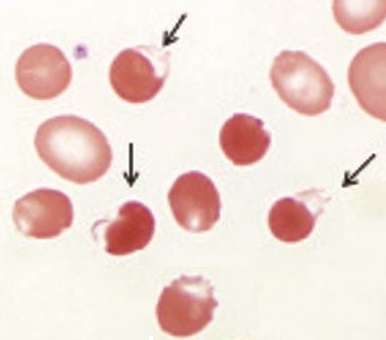
Other erythrocyte abnormalities are covered under Erythrocytes.
Aetiology
At-risk ethnic backgrounds include:
These are also (incidentally), generally Malaria-prone regions.
- Mediterraneans
- Sub-Saharan Africans
- Southeast Asians
- Indians
- Latin Americans
Clinical Features
Assessment
History:
Exam:
Investigations
Bedside:
Laboratory:
Imaging:
Other:
Diagnostic Approach and DDx
Management
- Cease trigger
- Supportive care
Resuscitation:
Specific therapy:
- Pharmacological
- Procedural
- Physical
Supportive care:
- H
- Transfusion
Disposition:
Preventative: