Head and Neck
| Component | Inspection | Palpation | Percussion | Auscultation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| General |
|
|||
| Respiratory |
|
|
|
|
| Cardiovascular |
|
|||
| Neurological |
|
|
||
| Endocrine and Metabolic | ||||
| Renal | ||||
| Gastrointestinal |
|
|||
| Haematological | ||||
| Integumentary | ||||
| Trauma |
|
|||
| Infective |
|
|||
| Malignant | ||||
| Toxic | ||||
| Immune |
|
|||
| Congenital | ||||
| Obstetric |
Features
General
- Central cyanosis
Blue-ish mucosa seen with:- Hypoxaemia (<80%)
- Methaemoglobinaemia (>1.5%)
- Sulfhaemoglobinaemia (>0.5%)
- Pseudocyanosis
Blue-ish mucosa in absence of hypoxaemia or other haemoglobinopathy, dur to:- Heavy metal intoxication
- Silver
- Gold
- Drug therapy
- Amiodarone
- Minocycline
- Chloroquine
- Phenothiazines
- Heavy metal intoxication
Respiratory
- Stridor
High pitched, harsh, inspiratory sound due to partial upper airway obstruction.- >80% stenosis may be heard unaided, and signify severe airway obstruction
Rapidity of onset indicates the aggressiveness of treatment required. - Lower-grade stenoses may be appreciated with a stethoscope
- >80% stenosis may be heard unaided, and signify severe airway obstruction
Neurological
- Mydriasis
Pupillary dilation may occur due to:- Optic nerve injury
- Amaurosis
- Isolated midbrain lesion
- Intoxication
- CN III compression
- Uncal herniation
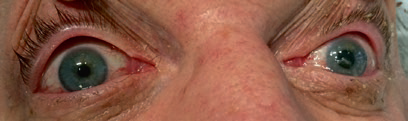
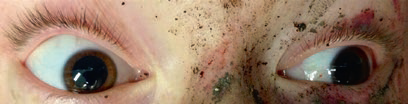
- Meningism
- Neck stiffness or pain on passive lateral rotation
Gastrointestinal
- Spider naevi
Central arteriole with radial spreading vessels, with local erythema. The naevi blanche on compression, and refill from the central arteriole. Spider naevi occur in:- Alcoholic liver disease
- Other liver disease
- Hepatitis C infection
- Vasodilatory states
- Pregnancy
- Malnutrition
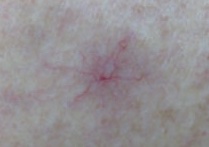
- Icterus
Becomes evident when bilirubin >85-135μmol/L.
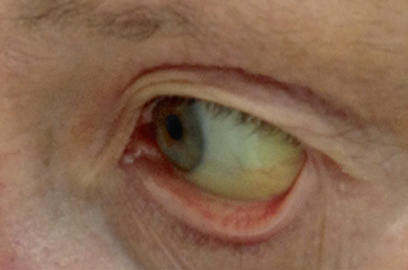
Trauma
- Conjunctival haemorrhage
Capillary rupture due to ↑ venous pressure.
References
- Foot C, Steel L, Vidhani K, Lister B, MacPartlin M, Blackwell N. Examination Intensive Care Medicine. Elsevier Australia; 2011. (Examination series).
- Dünser MW, Dankl D, Petros S, Mer M. Clinical Examination Skills in the Adult Critically Ill Patient. Springer International Publishing; 2018.