Leukocytes
White cell indices reported on a full blood exam may include:
Abnormalities
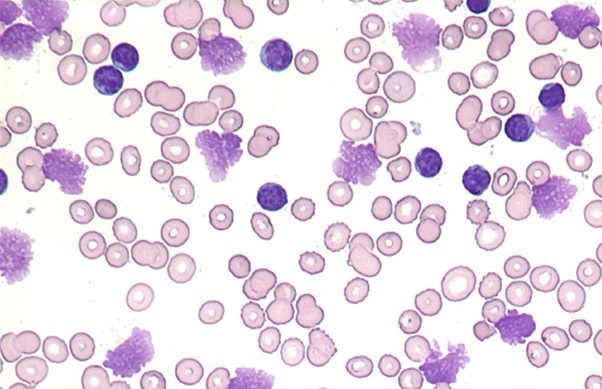
- Immature Granulocytes (3-5%)
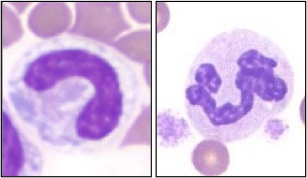
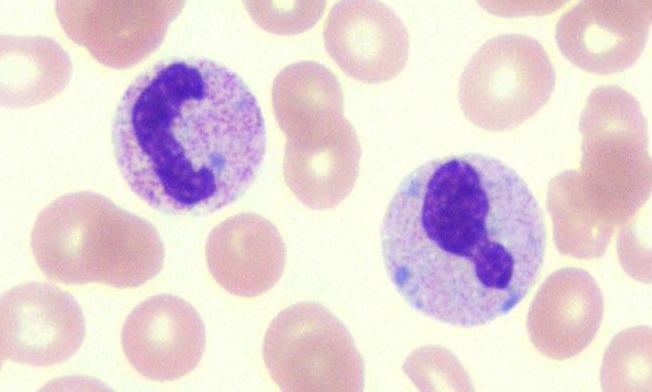
An ↑ in immature granulocytes granulocytes released from the bone marrow, which:- Commonly includes “band” cells, which have not yet developed the segmented nucleus of an adult neutrophil
- Is described as a left shift, which reflects an ↑ in the ratio of immature:mature neutrophils
- Occurs in response to either:
- Inflammation
- Necrosis
- Infection
- Sepsis
- Anaemia
- Haemorrhage
- Bone marrow infiltration
- Inflammation
Left-shift of neutrophils is an ↑ in immature (“band”) neutrophils in blood, as an active response of bone marrow to infection or inflammation.
- Toxic Changes
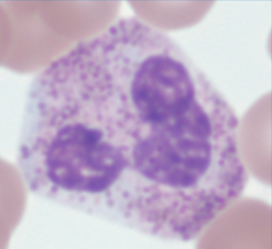
Toxic changes requires two of the following:- Toxic granulation
Dark, coarse, peroxidase-containing granules that have not been lost with neutrophil maturation. Indicate ↑ release, due to:- Infection
- Inflammation
- Burns
- Trauma
- G-CSF
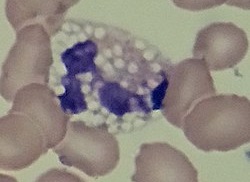
- Toxic vacuolation
Presence of (abnormal) neutrophil vacuoles, indicating active phagocytosis. Occur with:- Bacteraemia
- Fungaemia
- Liver failure
- G-CSF
- Artifact
- Döhle bodies
Blue cytoplasmic inclusions, which are the remnant of the rough endoplasmic reticulum. Occur with:- Leukemoid reactions
- Exotic infections
- Syphilis
- Typhoid
- Tuberculosis
- Toxic granulation
- Leukemoid Reaction
Extreme leukocytosis (>50×103/mL) occurring for a reason other than leukaemia. Features:- Predominantly neutrophils
- Marked left shift
- Usually due to:
- Infection
- Inflammatory
- Drugs and toxins
- Malignancy
- Haemorrhage
- Haemolysis
| Category | Examples |
|---|---|
| Infective |
|
| Inflammatory |
|
| Drugs and Toxins |
|
| Malignancy |
|
| Haemorrhage and Haemolysis |
|
| Other |
|
- Smudge Cells
Destruction of fragile lymphocytes during blood smear preparation, indicative of CLL.
References
- Sakka V, Tsiodras S, Giamarellos-Bourboulis EJ, Giamarellou H. An update on the etiology and diagnostic evaluation of a leukemoid reaction. European Journal of Internal Medicine. 2006;17(6):394-398. doi:10.1016/j.ejim.2006.04.004