Recruitment
A recruitment manoeuvre is a sustained, transient ↑ in airway pressure above normal tidal ventilation pressure, and sustained beyond a normal inspiratory time, which aims to open collapsed alveoli and small airways so they are able to participate in gas exchange.
Indications
Hypoxaemia with evidence of recruitable lung:
- Clinical suggestion of collapse
- Post-intubation
- Post-bronchoscopy
- Radiographically recruitable lung
Evidence of volume loss implying collapse rather than consolidation. - PEEP-responsive ARDS
How to identify this subgroup remains unclear.
Contraindications
- High risk of barotrauma:
- Bullous lung disease
- Previous PTHx
- Current PTHx
- CVS instability
Principles
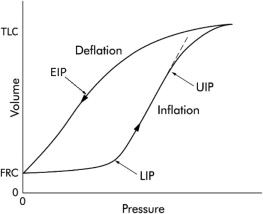
Lung parenchyma collapses in a heterogenous fashion. Alveoli:
- Open when pressure exceeds the critical opening pressure
- Collapse when pressure falls below critical closing pressure
- Critical closing pressure is less than the critical opening pressure
Application of PEEP above the critical closing pressure keeps alveoli open.
- Critical closing pressure is less than the critical opening pressure
- Will tend to distribute pressure first to well-aerated lung
This may lead to over-distention of healthy lung, prior to recruitment of lung units with poor compliance
Recruitment manoeuvres:
- Are cheap
- Have been shown to improve:
- Oxygenation
- Gas exchange
- Inflammatory markers
- Are described with a wide variety of techniques:
- 30cmH2O for 30-60s
Safe, moderately effective. - 40cmH2O for 40s
- Pip at 50cmH2O, aiming PEEP above the upper inflection point on the pressure-volume loop
- Titration of Pip up to 40cmH2O
- Staircase recruitment
- 30cmH2O for 30-60s
No recruitment strategy has been shown to be superior.
Practice
Appropriate in carefully selected patients. Considerations:
- High chance of recruitable lung
- Low risk of harm
- Recruitment strategy
- I have found 30cmH2O for 60s or 40cmH2O for 40s, abandoning if hypotension or hypoxia result, to be safe and effective
- My experience with staircase recruitment is that it causes significant haemodynamic instability without much additional benefit in oxygenation
Complications
Risks relate to significant ↑ airway pressure:
- Requires sedation/paralysis
- Barotrauma
- Pneumothorax
- Pneumomediastinum
- Cyclic atelectasis
Re-collapse after cessation of recruitment.
- Cardiovascular instability
- ↑↑ RV afterload
- ↓ VR
Key Studies
- ART (2017)
- ~1000 adults with moderate-severe ARDS requiring mechanical ventilation, without high risk of barotrauma or escalating vasoactive requirements
- Multicentre (120!), unblinded, allocation concealed, block randomised trial
- Open lung vs. control
- Open lung
- PCV with driving pressure of 15cmH2O
- Muscle relaxation applied
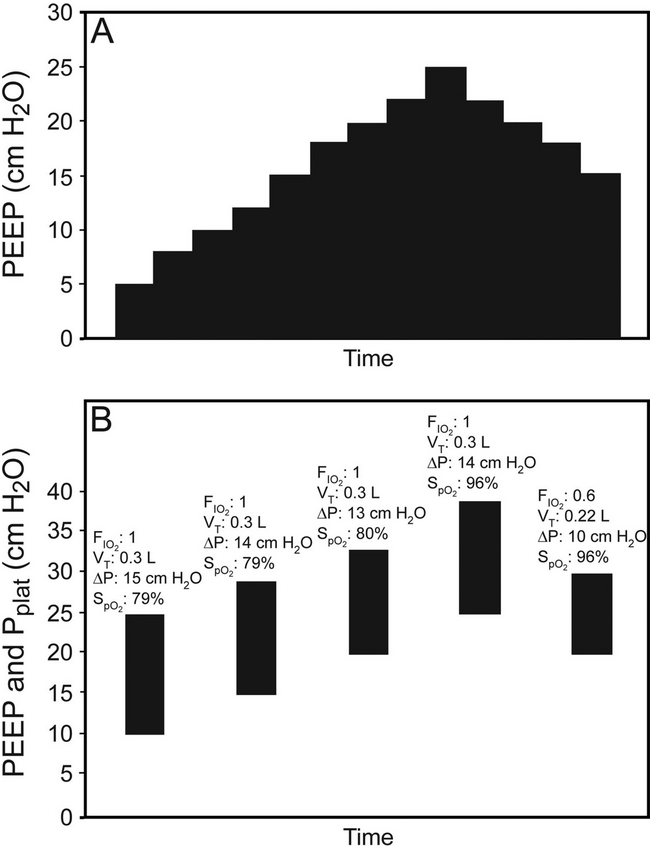
- Staircase recruitment up to PEEP of 45cmH2O
- PEEP down-titrated in 3cmH2O increments, with measurement of static compliance at leach level
Level with highest lung compliance noted. - Further recruitment at PEEP 45cmH2O of PEEP
- New PEEP set to level at maximal compliance + 2cmH2O
- Control
- Conventional ARDSnet ventilation
- Both groups managed with VCV at 6mL/kg with safe lung ventilation
- Refractory hypoxaemia managed with proning, iNO, or VV ECMO
- Pressure support attempted once PEEP <14cmH2O
- Open lung
- ↑ Mortality in open lung group (55.3% vs 49.3%, p=0.04)
- Secondary outcomes showed the open lung group had ↑ 6 month mortality, ↓ ventilator free days, and more pneumothoraces requiring drainage
- Compliance in open lung group did not significantly ↑ following recruitment
- Recruitment manoeuvre had to be abandoned in 15% due to hypotension or hypoxia
- Most patients only had one recruitment manoeuvre
- Indiscriminate aggressive recruitment manoeuvres are harmful in moderate-severe ARDS, but this does not rule out benefit in select subgroups
References
- Writing Group for the Alveolar Recruitment for Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome Trial (ART) Investigators. Effect of Lung Recruitment and Titrated Positive End-Expiratory Pressure (PEEP) vs Low PEEP on Mortality in Patients With Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA. 2017;318(14):1335-1345. doi:10.1001/jama.2017.14171
- Cavalcanti AB, Amato MBP, de Carvalho CRR. Should the ART trial change our practice? J Thorac Dis. 2018;10(3):E224-E226. doi:10.21037/jtd.2018.02.25
- Hess DR. Recruitment Maneuvers and PEEP Titration. Respiratory Care. 2015;60(11):1688-1704. doi:10.4187/respcare.04409