Hands
| Component | Inspection | Palpation | Percussion |
|---|---|---|---|
| General | |||
| Respiratory |
|
||
| Cardiovascular |
|
||
| Neurological | |||
| Endocrine and Metabolic | |||
| Renal | |||
| Gastrointestinal |
|
||
| Haematological | |||
| Integumentary |
|
||
| Trauma | |||
| Infective |
|
||
| Malignant | |||
| Toxic | |||
| Immune |
|
||
| Congenital | |||
| Obstetric |
Features
Respiratory
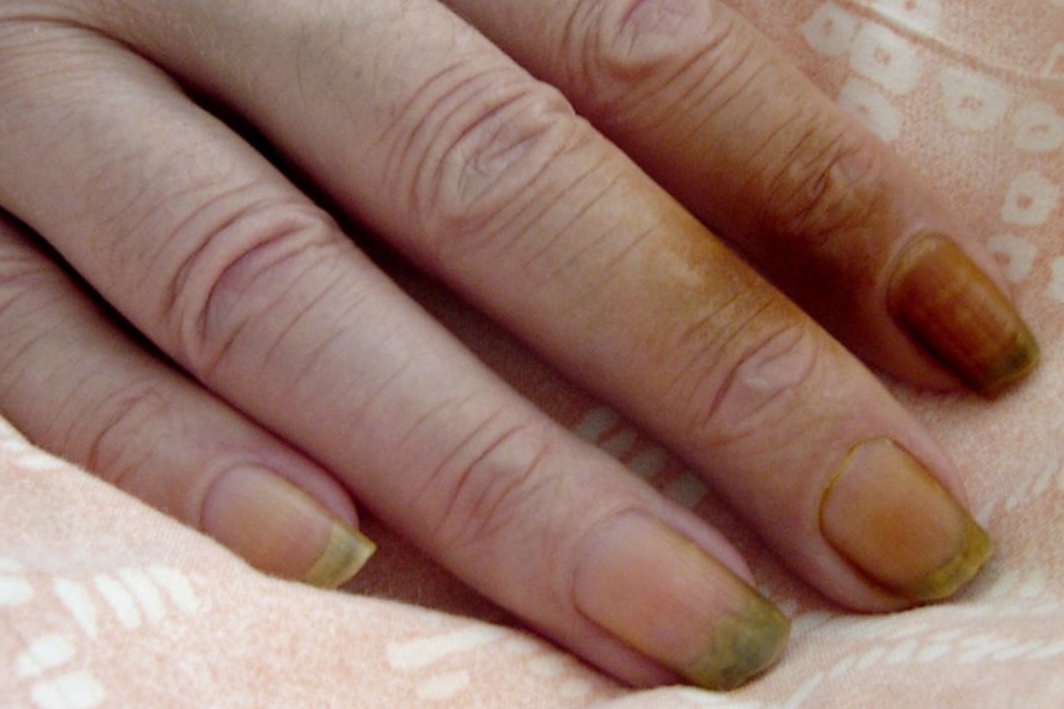
- Nicotine staining
Indicative of smoking.
- Clubbing
Loss of the nail bed angle and soft tissue swelling at the tips of the digit.
The normal nail bed angle is <140–160°, and is (was?) known as the Lovibond angle.
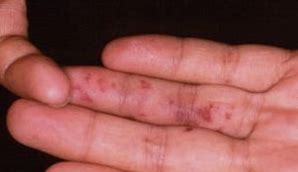
- Janeway lesions
Red-purple, non-tender, haemorrhagic lesions on the palms and soles associated with septic microembolism, particularly S. Aureus endocarditis. Typically last days-weeks.
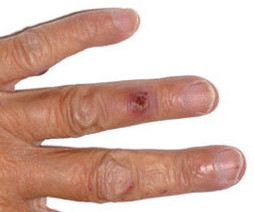
- Osler’s nodes
Tender, raised red-purple lumps, usually with a pale centre, and associated with septic microembolism, classically bacterial endocarditis. Typically last from hours to a few days.
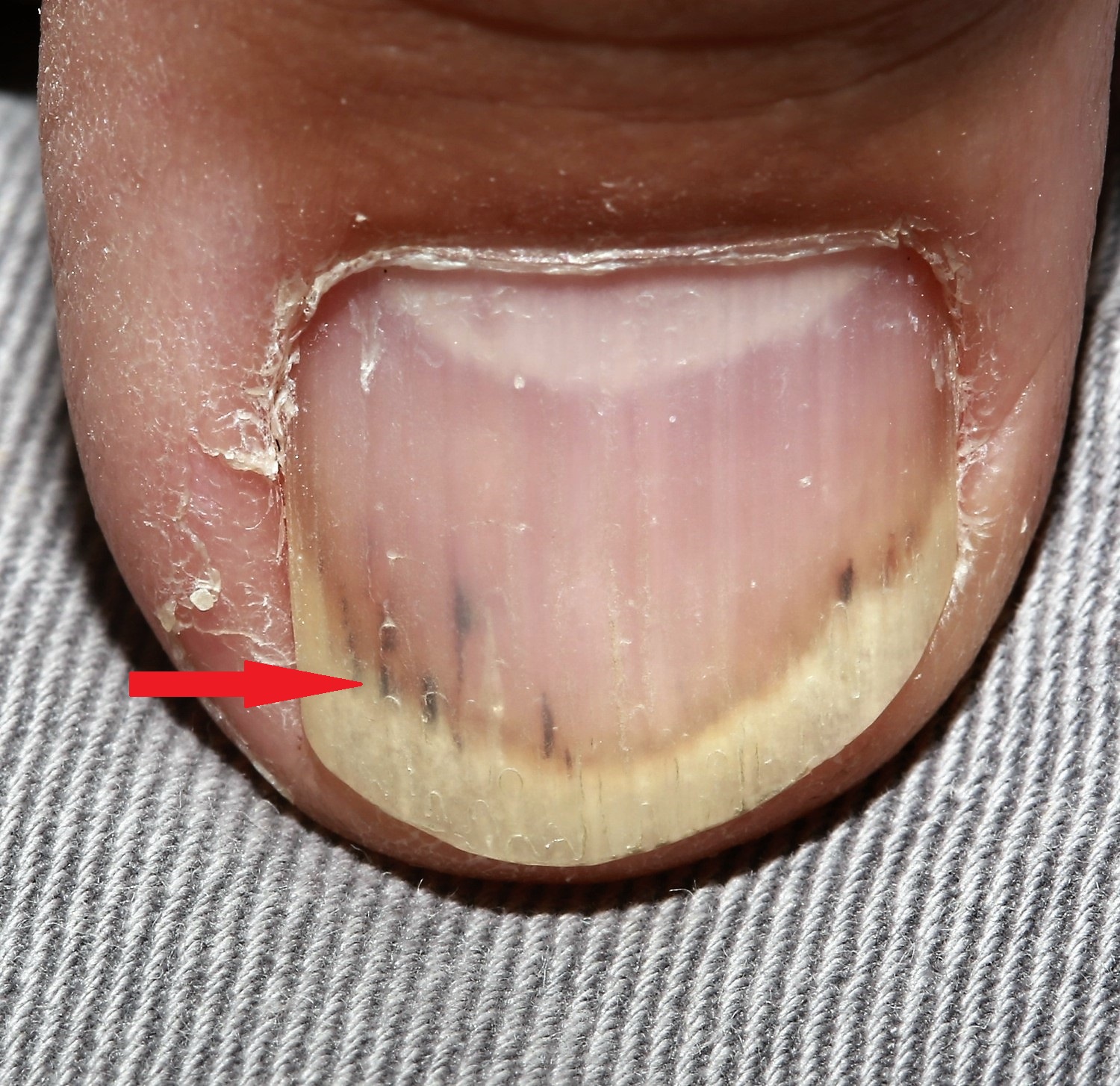
- Splinter haemorrhage
Longitudinal, red-brown haemorrhage under the finger nail. Associated with:- Trauma
- Endocarditis
- Meningococcal infection
- Histoplasmosis
References
- Foot C, Steel L, Vidhani K, Lister B, MacPartlin M, Blackwell N. Examination Intensive Care Medicine. Elsevier Australia; 2011. (Examination series).
- Dünser MW, Dankl D, Petros S, Mer M. Clinical Examination Skills in the Adult Critically Ill Patient. Springer International Publishing; 2018.