Physiotherapy
Roles of physiotherapy in the ICU:
- Respiratory physiotherapy
- Therapeutic hyperinflation
Aims to ↑ recruitment and ↓ airway resistance. Can be:- Manual
Use self-inflating circuit to deliver >150% of Vt. - Ventilator-assisted
Use ventilator to ↑ VT by 200mL increments until Pip of 40cmH2O.
- Manual
- Active Cycle of Breathing Technique
Controlled breathing to ↑ secretion clearance in spontaneously ventilating patients. - Suction
Remove secretions via ETT. - Chest shaking
Oscillatory movement during expiration ↑ mucociliary clearance. - Positioning
- Sitting up to optimise V/Q matching
- Gravity-assisted positioning
Adjust patient to position bronchopulmonary segment perpendicular to gravity to ↑ secretion drainage. - Side-to-side turning
↓ VAP. - Proning
↑ Oxygenation and ↓ mortality in ARDS.
- Therapeutic hyperinflation
- Early rehabilitation
Aims to ↑ independence and ↓ severity of ICU-acquired weakness. Techniques exist for:- Bed
Cycle ergometry, passive movements, electrical stimulation, hoisting. - Chair
Postural exercises, balance and proprioception, core stability. - Standing
Marching, stairs, walking.
- Bed
- Positioning aids
↓ Contracture formation.
Key Studies
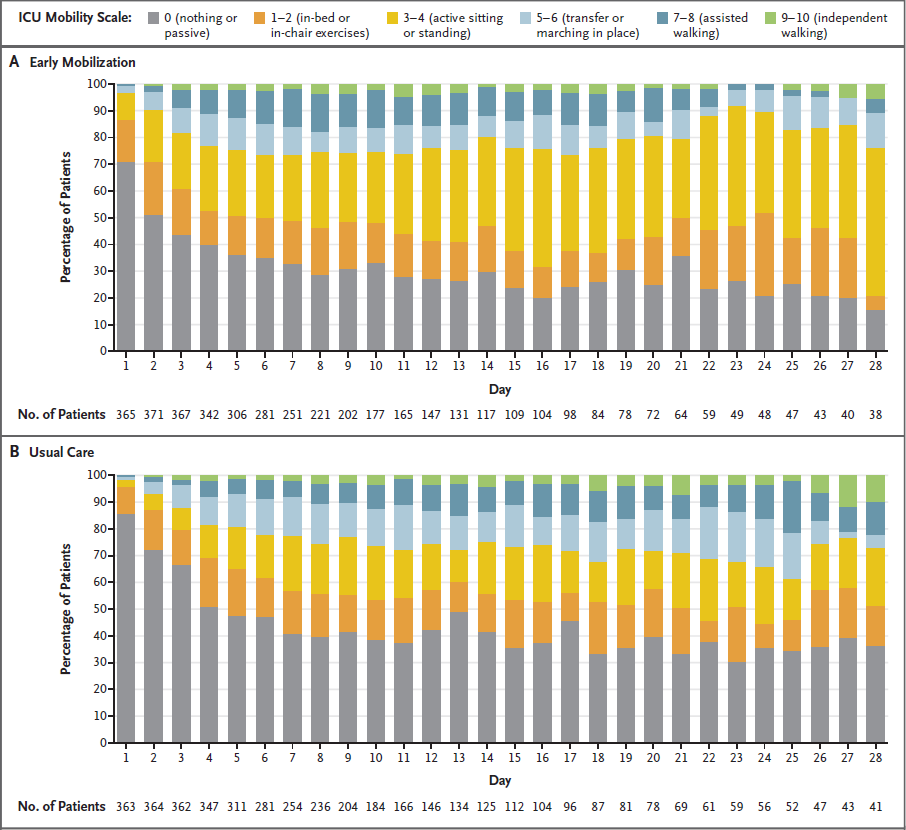
- TEAM (2022)
- 750 adult ventilated ICU patients
- Early mobilisation vs. usual care
- Early mobilisation: highest level of activity for the longest time on the lowest amount of sedation
- Usual care still included reasonably early mobilisation
- No significant mortality difference
- Standing and walking occurred 1-2 days earlier in the early mobilisation group
- More adverse events in the early mobilisation group
References
- Bersten, A. D., & Handy, J. M. (2018). Oh’s Intensive Care Manual. Elsevier Gezondheidszorg.
- Early Active Mobilization during Mechanical Ventilation in the ICU. New England Journal of Medicine. 2022;387(19):1747-1758.